Everything You Should Know About Diabetes
This blog/post may contain links to third party merchants. Smarty earns commissions on purchases you make using these links.
Diabetes is a group of diseases caused when your sugar metabolism is low, and your body fails to control the glucose levels in the bloodstream. Diabetes is usually a result of poor lifestyle habits, obesity, or improper diet. It also can be hereditary or caused due to any external injury to the pancreas. According to CDC, “more than 37 million people in the United States have diabetes, and 1 in 5 of them don’t know they have it. Diabetes is the 7th leading cause of death in the United States“.
There is no specific cause of diabetes, but generally, it occurs when the insulin levels are disturbed. Our body gets energy from the food we intake when the carbohydrates are broken down into glucose. The cells absorb this glucose through a hormone called insulin, produced in the pancreas. When insulin production is restricted or reduced, the glucose doesn’t enter the cells and accumulates in the bloodstream. This increases the glucose levels in the blood and might lead to severe complications if precautions are not taken.
Types of Diabetes
1. Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, also known as auto-immune diabetes, is usually a hereditary disorder commonly seen in children or young adults. In this type of disorder, the body refuses to produce insulin, and the glucose stays accumulated in the bloodstream, raising the blood sugar levels constantly. According to the CDC, 5-10% of total diabetic patients have Type 1 diabetes, which can be regulated with lifestyle changes.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is caused due to obesity and poor lifestyle. In this type, the pancreas produces insulin, but the cells fail to take up the insulin, and the blood sugar levels increase. According to the CDC, 90-95% of total diabetic patients have Type 2 diabetes, which generally occurs in older people, but it has become common even in young adults.
3. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is caused when a pregnant woman faces difficulty in managing her insulin levels in the body. This condition is temporary but might increase the chances of developing Type 2 diabetes in the later stages of her life or in her child.
4. Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a condition where the blood glucose level isn’t in its optimal range, i.e., higher than the normal range but lower than type 2 diabetes. CDC reports show that ninety-six million US adults have prediabetes, and more than 8 in 10 don’t know they have it. Prediabetics generally don’t show any symptoms and are mostly unknown unless tested. If not managed well, this condition can lead to Type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Symptoms of Diabetes vary from person to person, depending on the type of diabetes, range of blood sugar levels, diet, and lifestyle patterns. The following are the common symptoms of diabetes –
- Excess Thirst and Sweat – A diabetic patient feels excessively thirsty and might sweat heavily.
- Frequent Urination – When you have high glucose in your bloodstream, your kidneys work overtime to release waste from your body, making you urinate often.
- Fatigue – With increased blood sugar levels, the insulin doesn’t reach the target cells, and your organs might not get sufficient energy, leading to dizziness and fatigue.
- Blurred Vision – Diabetes may damage your eyes and might cause blurred vision.
- Headache – Increased blood sugar levels might lead to headaches.
- Weight Loss – With diabetes, your body functioning is distorted, and you might experience unexpected weight loss.
- Increased Hunger – Diabetic patients are said to be more hungry than others, and eating several meals in small portions is advisable.
- Delay in Healing Wounds – Diabetes reduces your body’s ability to clot the blood. If you have scars or cuts, it takes longer than usual to heal.
Health Risks of Diabetes
Heart Problems
Diabetes may result in heart disease, strokes, or chest pain by narrowing arteries and making it difficult to pump blood.

Kidney Problems
High blood glucose levels can damage glomeruli that help filtrate waste in kidneys and lead to kidney failure if precautions are not taken.

Dental Problems
Diabetes can reduce the blood supply to your gums and bones and cause cavities and infections in the gums and bones. You might have bleeding and sore gums with prolonged bad breathe when your sugar levels are high.

Brain and Nervous System Damage
High blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels that carry oxygen and can eventually damage brain cells (atrophy). This can lead to dementia.
Foot Problems
High blood sugar levels for a prolonged time might reduce the blood flow and lead to nerve damage in the feet, resulting in infections and foot ulcers. If it becomes serious, this condition might lead to leg or foot amputation. Keep your feet protected with diabetic socks to ease the blood circulation in your feet and prevent blisters or ulcers.
Eye Problem
High sugar levels might damage blood vessels in the retina, and in the long term, it might lead to blindness. According to WHO, nearly 1 million people became blind due to diabetes.
Depression
Poor lifestyle habits and high glucose levels can influence feelings of anxiety, restlessness, or loss of energy and can lead to depression.

Management of Diabetes
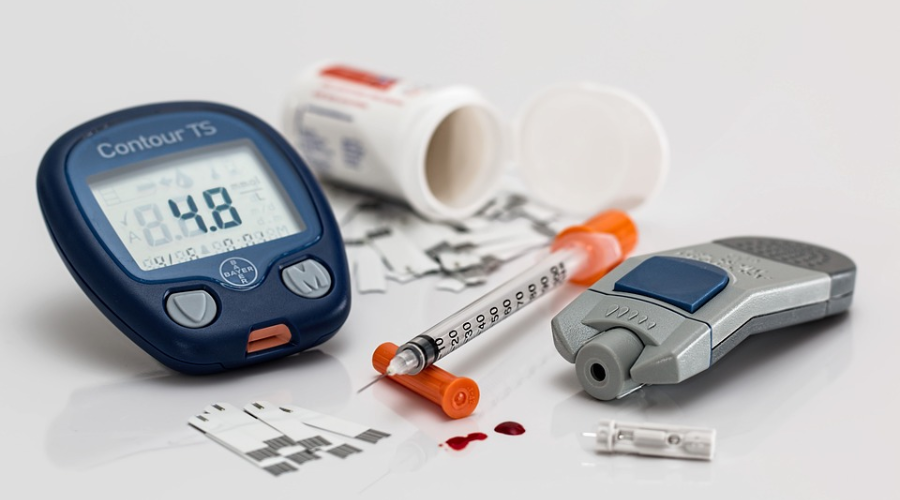
- Keeping yourself active and incorporating exercise in your daily routine helps you stay fit and avoid obesity. Walking, yoga, cardio, or strength exercises for 30 minutes a day, five days a week, can help you reduce complications and spikes in sugar levels.
- A healthy diet with whole grains, beans, lentils, fruits & vegetables, lean meat, fish, dairy products, etc., can help you keep your blood sugar in check.
- Check your blood sugar levels regularly. Recommended blood glucose level while in the fasting stage is 80-130 mg/dL, and two hours after a meal is 180 mg/dL. Anything more or less indicates you need to visit your doctor. You can get your personalized diabetes testing kit from Walgreens.
- Take the medications regularly. This will help you keep your sugar levels in control. And when taking insulin dosage (especially in Type 1 diabetes), do not miss it by any chance.
- Have regular health check-ups to record your body functioning and check for blood sugar levels.
- Check your blood pressure and keep it in control. Avoid excess salt and keep the blood pressure below 140/80 mm Hg to avoid health risks.
- Stay stress-free by practicing meditation, breathing exercises, or yoga.
- Quit smoking as the smoke can dilate your blood vessels and make it difficult to pump blood into different organs, leading to heart attacks or failure of organs.
Also Read: Heart-Healthy Recipes That Are Easy and Yummy!
With the motive of educating people about diabetes and spreading awareness, World Diabetes Day is celebrated worldwide on November 14. Check for the symptoms and take precautions before it’s late. Let’s spread awareness and battle the cluster of diseases caused by diabetes.







